Useful links:
Git and Github are two different things! Unix systems like Linux and Macbooks already have Git, but it must be installed on Windows.
Git is a memory card for code
- Just like a video game, you save your progress as you go so that you can respawn once you die (nobody was injured in the making of this documentation, maybe)
Commands
-
Initialize a folder with Git
git innitinstall a memory card
-
Choose files to save your progress (staging)
-
git add file.txtsave a file -
git add .save everything
-
-
Save changes (commit)
git commit -m 'adding files to the repository'
-
Check saves
git log
-
Load a save
-
Copy the hash from the save log
git checkout [hashcode-here]
-
Github = Bitbucket = Gitlab = Website for Git for sharing with others
pushis uploading commits to Github repositorypullis downloading updates to a repository from Github
Branches
- A save file for another character/player without affecting the original save!
Pull Request
- Here is my
branchwith my changes. What do you think?
Merging
- good changes were made, saved, and committed to a branch—let’s merge it into main
| Merge Type | Diagram |
|---|---|
| Merge | 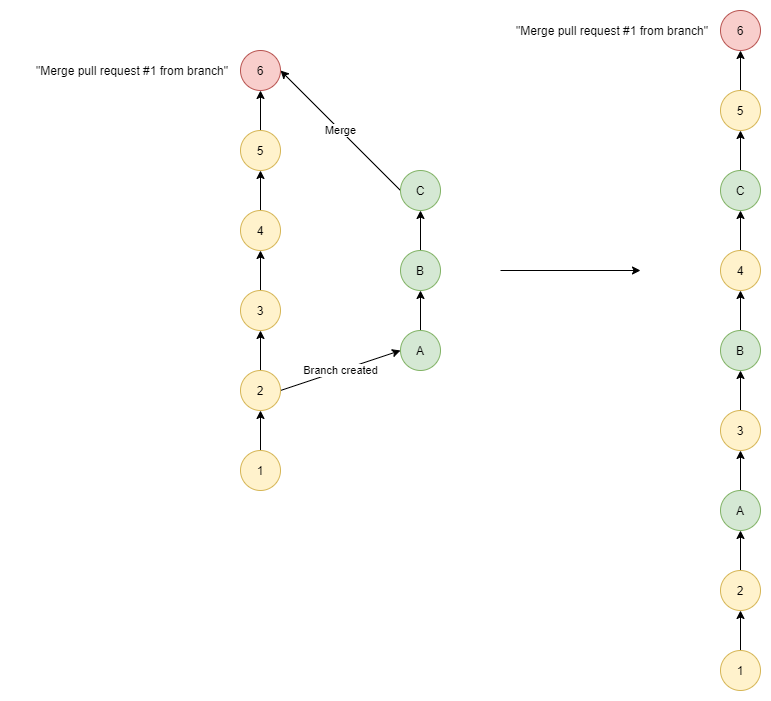 |
| Fast-Forward | 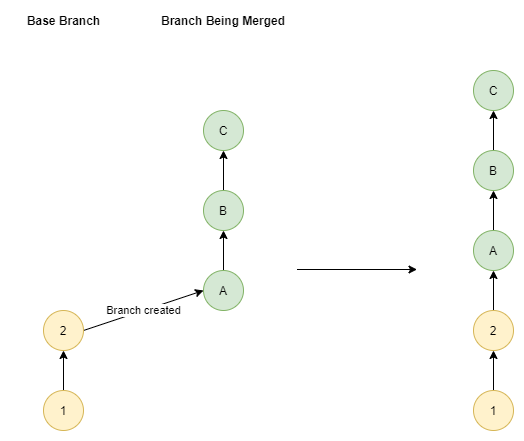 |
| Squash | 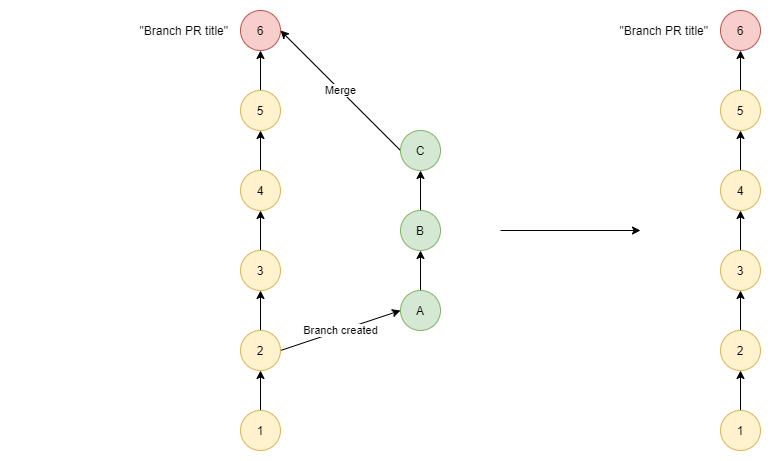 |
| Rebase | 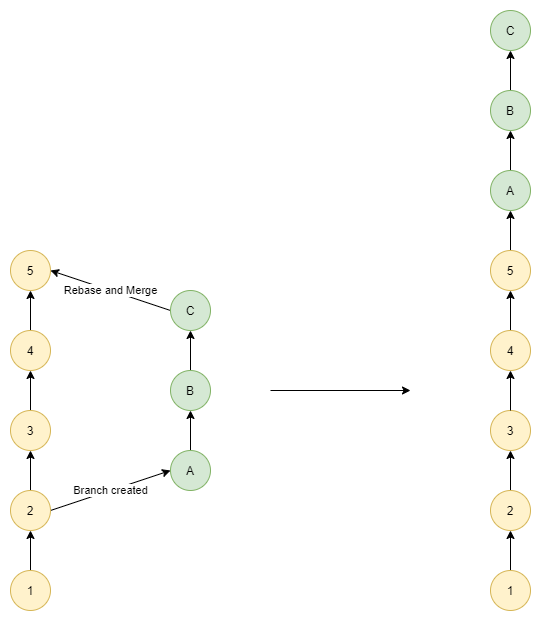 |
Diagrams from https://lukemerrett.com/different-merge-types-in-git/
Commits
underconstruction Conventional Commits Semantic Versioning 2.0.0
Reverting commits
We’ll use
git logto determine which commits he did. It’s up to you to determine which commit to “stop” at, though.First,
git logto pull a listing of all of the commits that they’ve done on a specific branch:
git log --graph --author="Tom" --oneline --decorate --pretty <branch>From that, you can get a list of all of Tom’s commits.Now, you can use
git revertto specify a range of commits to revert. Suppose that the last commit he did wasffffff, and the first he did wasaaaaaa, you’d write this:
git revert aaaaaa^..ffffff
Then, to exit the VIM editor in the terminal:
type `esc` then `:wq`